When it comes to modern farming techniques, aeroponics and hydroponics stand at the forefront of innovation. These soil-less cultivation methods have revolutionized the way we grow plants, offering numerous advantages over traditional soil gardening. In this first part of our exploration, we’ll delve into the basics of aeroponics and hydroponics, examining the two systems, how they differ and the unique benefits they bring to the world of agriculture.
Aeroponics: The Art of Suspended Growth
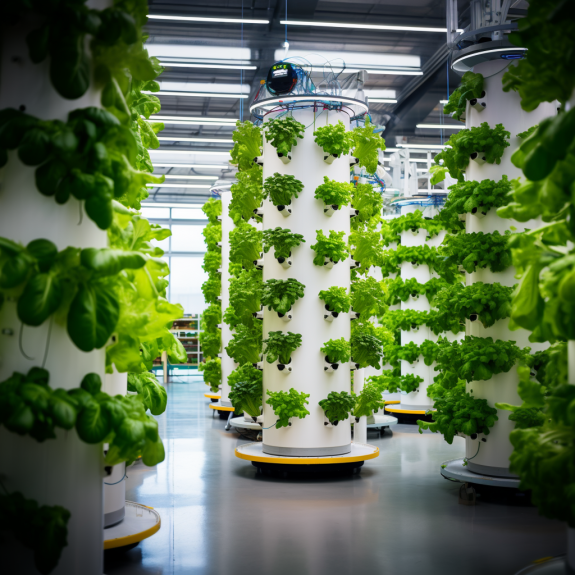
Aeroponics is an innovative and efficient way of growing plants that is gaining popularity among farmers and horticulturists. Unlike conventional soil-based farming, aeroponics involves suspending the plant roots in air and providing nutrients and moisture through mist or spray. This method offers several advantages, such as faster growth rates, higher yields, and reduced water usage. Additionally, aeroponics can be used to grow crops in areas with poor soil quality or limited space. With its potential to revolutionize the agriculture industry, aeroponics is an exciting area of research and development. Additionally, aeroponics systems are a great way to save space as they can be set up vertically, allowing for more plants to be grown in a smaller area.
Faster Plant Growth
Aeroponics systems are a highly efficient way to grow plants as they promote rapid growth by providing plants with direct oxygen and nutrient nourishment to their roots. This leads to faster growth rates compared to traditional soil gardening, making it an excellent option for those who want to produce more crops in a shorter amount of time.
Higher Yields
The ability to supply nutrients directly to the plant roots in an all aeroponic growing system results in higher yields. Commercial growers have embraced this method for its ability to produce more crops in less space.
Minimal Nutrient Waste
Aeroponics systems use fewer nutrients and water compared to hydroponic systems. With careful water temperature regulation and precise nutrient delivery, there is minimal waste, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Healthier Plants
Plants grown in aeroponic systems are healthier and more robust due to the absence of soil-borne diseases and pests, as well as optimal nutrient absorption resulting in vibrant and vigorous plants. Aeroponic systems offer a unique way to grow plants that is both healthier and more effective than traditional methods. By eliminating the use of soil, plants are protected from soil-borne diseases and pests, ensuring they can grow stronger and more robust. Additionally, the optimal nutrient absorption provided by aeroponic systems results in vibrant and vigorous plants that are able to thrive in any environment.
Hydroponics: Harnessing the Power of Water
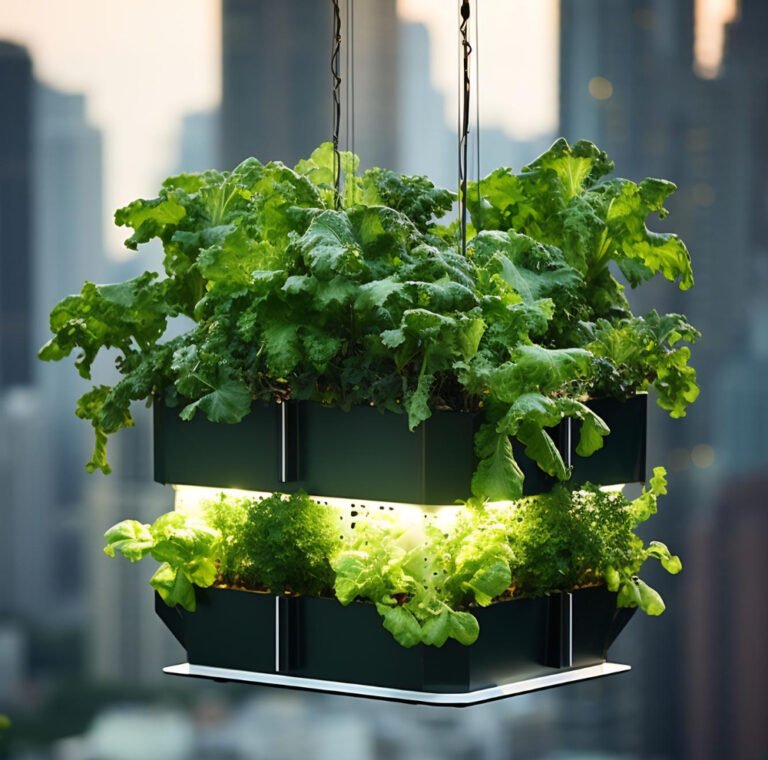
Hydroponics is a soil-free method of cultivating plants in nutrient-rich water that has gained popularity in recent times due to its numerous benefits. This innovative technique not only produces healthier plants but also maximizes space utilization, making it a favored choice among farmers and gardeners alike. In hydroponics, plants are grown in a controlled environment with the help of a nutrient solution, which provides all the necessary minerals and vitamins required for their growth. This method is not only efficient but also helps conserve water as it requires less water compared to traditional soil-based farming. With the rise of hydroponics, we can expect to see a revolution in the way we grow our food, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Versatility and Efficiency
Hydroponic systems can grow a wide variety of plants, from leafy greens to vine plants. They are also incredibly efficient in terms of space usage, making them suitable for urban farming and vertical gardening.
Precise Nutrient Control
In hydroponics, nutrient solutions are carefully measured and delivered directly to the plant roots. This precision allows for optimal nutrient absorption and eliminates nutrient waste.
Year-Round Cultivation
Hydroponic farming systems are not dependent on weather conditions. This means crops can be grown year-round, providing a consistent supply of fresh produce.
Resilience to Soil Limitations
In regions with poor or contaminated soil, hydroponics offers a viable alternative. It eliminates the need for arable land and the challenges associated with soil-based growing.
Hydroponics vs. Aeroponics: Key Differences
In our quest to understand these soil-less cultivation methods, it’s crucial to highlight some key differences between hydroponics and aeroponics. These distinctions can influence the choice of method for specific applications:
– Root Environment: Hydroponics immerse plant roots in nutrient-rich water solution, while aeroponics suspends the roots in air and delivers nutrients via mist or spray.
– Water Usage: Hydroponics generally consumes more water than aeroponics due to the constant submersion of plants roots throughout. Aeroponics, with its precise misting system, uses water more efficiently.
– Nutrient Delivery: In hydroponics, nutrient solutions are circulated through the system, while in aeroponics, they are misted onto the roots. This affects nutrient absorption rates.
– Speed of Growth: Aeroponics tends to promote faster plant growth compared to hydroponics, thanks to the increased oxygen supply and direct nutrient delivery.
– Environmental Impact: Aeroponics is known for its minimal nutrient waste and lower water consumption, making it an environmentally conscious choice.
The Downsides of Aeroponics and Hydroponics
In our exploration of soil-less cultivation methods, we’ve delved into the advantages of aeroponics and hydroponics. However, no system is without its drawbacks. In this section, we’ll shine a light on the disadvantages of both aeroponics and hydroponics to provide a balanced perspective.
Disadvantages of Aeroponics
1. Vulnerability to Power Outages
Aeroponic systems heavily rely on power to maintain the misting or spraying of nutrient-rich water. During power outages, plants may suffer from the lack of essential nutrients and moisture, potentially jeopardizing crops.
2. Complex Setup and Ongoing Running Costs
Setting up an aeroponic farming system can be more complex and costly compared to traditional soil gardening. Moreover, the ongoing energy and maintenance costs can add up over time.
3. Greater Attention Required
Aeroponic systems demand careful monitoring and maintenance. The precise regulation of nutrient-rich water and misting systems can be time-consuming.
Disadvantages of Hydroponics
1. Higher Water Usage
Hydroponic systems generally consume more water than aeroponics due to the continuous submersion of plant roots. In regions with water scarcity, this can be a significant drawback.
2. Risk of Nutrient Imbalance
Maintaining the correct balance of nutrients in hydroponic systems can be challenging. If not carefully managed, it can lead to nutrient imbalances that harm plant growth.
3. Potential for Disease Spread
While hydroponics reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases, it doesn’t eliminate the possibility of diseases spreading through water systems. Proper sanitation is crucial to prevent such issues.
How Much Faster Is Aeroponics Than Hydroponics?
One of the key questions often asked is about the speed of plant growth in aeroponics compared to hydroponics. Aeroponics is indeed known for promoting faster growth, primarily due to the increased oxygen supply to plant roots and the direct delivery of nutrients. While growth rates can vary depending on the specific plant species, it’s common to observe growth rates in aeroponics that are 20-30% faster than hydroponics.
But it’s important to note that faster growth doesn’t necessarily mean better quality. The speed of growth can sometimes affect the taste and texture of certain crops. Growers need to strike a balance between speed and quality to achieve the desired results.
Aeroponics is better if you:
– Need rapid plant growth.
– Want to maximize space efficiency.
– Are concerned about water conservation and reducing nutrient waste.
– Are willing to invest in a more complex system.
Hydroponics is better if you:
– Require a versatile system that can grow a wide range of crops.
– Prefer a well-established method with a lower learning curve.
– Can provide consistent access to power and water.
– Are looking for a system that can operate in various environmental conditions.
Ultimately, the choice between aeroponics and hydroponics depends on your specific needs and priorities. Both methods have their strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice will vary from one situation to another.
Aeroponics vs Hydroponics: Summarizing the Key Differences
As we near the conclusion of our exploration into the world of hydroponic and aeroponic systems soil-less cultivation, let’s recap the essential distinctions between aeroponics and hydroponics. Understanding these differences is crucial when deciding which method is the right fit for your specific needs:
Nutrient Delivery: The Lifeblood of Growth
Aeroponics: In the realm of aeroponics, plants experience a nurturing dance with a finely tuned mist or spray of nutrient-rich water. This delicate embrace provides plant roots, suspended in the air, with their essential sustenance. The precision of this delivery mechanism resembles a symphony conductor leading an orchestra to create harmonious growth. However, this precise control necessitates vigilant monitoring.
Hydroponics: Hydroponics, in stark contrast, immerses plant roots in a continuous bath of nutrient-rich water solution. This submerged existence mirrors the steady flow of a river, providing nourishment to all plants within its domain. Hydroponics is renowned for its versatility and ability to accommodate a wide variety of plant species.
Water Usage: The Fluid Dilemma
Aeroponics: The world of aeroponics shines as an exemplar of water efficiency, leaving behind minimal wastage thanks to its intricate misting and drip systems. This approach resonates with a vision of a controlled, gentle rainfall nurturing your plants, efficiently quenching their thirst while conserving precious water resources.
Hydroponics: In contrast, hydroponics exhibits a tendency towards higher water consumption due to the perpetual immersion of plant roots. This surplus water consumption can pose a conundrum, especially in regions where water scarcity prevails.
Speed of Growth: The Race Against Time
Aeroponics: Renowned for its Usain Bolt-like sprint to growth, aeroponics leverages the boosted oxygen supply to roots and the direct infusion of nutrients. This sprint, however, may sometimes compromise the flavor and texture of certain crops due to its rapid pace.
Hydroponics: Hydroponics, by contrast, boasts a steady, reliable stride in plant growth, slightly trailing behind aeroponics in terms of speed. It is akin to a seasoned marathon runner, maintaining consistency while ensuring desirable crop quality.
Environmental Impact: The Ecological Footprint
Aeroponics: With its eco-conscious mindset, aeroponics leaves minimal ecological footprints. It treads lightly with its frugal nutrient usage and efficient water management, presenting itself as a responsible steward of the environment.
Hydroponics: While commendably efficient, hydroponics does leave a slightly larger ecological footprint compared to aeroponics due to its higher water consumption. It’s akin to a conscientious traveler who endeavors to minimize their impact but still leaves discernible traces.
Complexity: The Intricate Symphony
Aeroponics: The setup and ongoing maintenance of an aeroponic system can be likened to orchestrating a complex symphony. It demands dedication and meticulous attention to detail, making it ideal for those who relish the intricacies of cultivation.
Hydroponics: Hydroponics, by contrast, is a seasoned musician playing a familiar tune. Its well-established nature and lower learning curve make it accessible to a broader audience, including those who may be new to soil-less cultivation.
Versatility: The Adaptive Chameleon
Aeroponics: Aeroponics thrives in scenarios that require swift growth and optimal space utilization. It excels in situations where maximizing crop output in minimal space is paramount.
Hydroponics: Hydroponics is akin to a versatile artist with a wide palette of colors. It accommodates various plant species and environmental conditions, making it a flexible choice for diverse cultivation needs.
Crop Quality: The Gourmet Experience
Aeroponics: While it delivers speed, aeroponics may sometimes sacrifice the subtleties of crop taste and texture due to its accelerated growth.
Hydroponics: Hydroponics consistently delivers quality results, preserving the flavors and textures of crops with a meticulous touch.
Disease Risk: The Health Factor
Aeroponics: It reduces the risk of soil-borne diseases but remains vigilant against disease transmission through water systems, necessitating careful sanitation.
Hydroponics: Hydroponics carries a low risk of soil-borne diseases but still necessitates stringent sanitation practices to ensure the health of crops.
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ve illuminated the intricacies that define aeroponics and hydroponics, equipping you with a deeper understanding of these innovative cultivation methods. Armed with this knowledge, you are better prepared to make a well-informed decision on the path to soil-less cultivation.
Thank you for accompanying us on this enlightening journey, and remember: Aeroponics vs Hydroponics. Discover the pros, cons, and secrets behind these cutting-edge growing methods. Let’s unravel the science of soil-less cultivation together!
FAQs about Aeroponics vs Hydroponics
Is Aeroponics Better Than Hydroponics?
The choice between aeroponics and hydroponics depends on your specific needs and priorities. Aeroponics is better for rapid growth, space efficiency, and reducing nutrient waste. Hydroponics is ideal for versatility, steady growth, and reliability.
What Are the Disadvantages of Aeroponics?
Aeroponics has some drawbacks, including vulnerability to power outages, complex setup with ongoing running costs, and the need for meticulous attention to nutrient and water management.
How Much Faster Is Aeroponics Than Hydroponics?
Aeroponics can promote growth rates that are 20-30% faster than hydroponics. However, the exact speed of aeroponic plants growth, can vary depending on plant species and environmental factors.
Are Aeroponics Better Than Hydroponics?
Neither method is universally better; they each have their strengths and weaknesses. The choice should align with your specific goals, resources, and the types of crops you intend to grow.
In conclusion, whether you choose aeroponics or hydroponics, you’re embracing cutting-edge agricultural methods that offer numerous benefits over traditional soil gardening. By understanding the nuances of each system and weighing their pros and cons, you can make an informed decision to embark on your journey into the world of soil-less cultivation.
Thank you for joining us on this insightful journey, and remember: Aeroponics vs Hydroponics. Discover the pros, cons, and secrets behind these cutting-edge growing methods. Let’s unravel the science of soil-less cultivation together!